Peptic Ulcer

A very painful and very common affliction, a peptic ulcer is an open sore that has erupted within the stomach lining. Also called ulcus pepticum, peptic ulcer disease, and PUD, a peptic ulcer consists of an area within the stomach lining that contains a high amount of acid, creating the painful effect that brings attention to the issue.
It has been a long standing and common belief that these peptic ulcers are caused by diet and stress, yet it has been found that these ulcers are caused by a bacterial infection, Helicobacter pylori, which thrive in the stomach acids. 80% of cases are attributed to this bacterium.
OTC Medicine
Aspirin and NSAID medications can also cause, as well as worsen these ulcers. There are 4% of cases that can be attributed to a malignant tumor, causing the need for multiple biopsies in order to exclude cancer as the cause for the ulcer.
As treatments differ for peptic ulcer disease, the difference depends on the type of ulcer and the aggression by which it is affecting the stomach. Choosing the best treatment option can be either a home remedy or a prescription medication that is discussed with your health care provider. The most serious cases of peptic ulcers require more aggressive measures, which too are best discussed with a professional health care provider.
Peptic Ulcer? Get Remedies Fast!
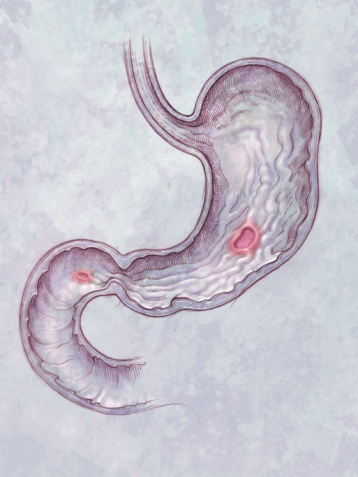
There are four main classifications of peptic ulcers that are categorized by their location
- Gastric ulcer
- Duodenal ulcer
- Oesophageal ulcer
- Meckel’s Diverticulum ulcer
There are also five types according to the actual ulcers present:
- Type I: peptic ulcer located along curve of stomach
- Type II: one gastric and one duodenal ulcer present
- Type III: Presence of prepyloric ulcer
- Type IV: Presence of proximal gastroesophageal ulcer
- Type V: Ulcer located anywhere
Symptoms
There are several symptoms of a peptic ulcer, all alerting to the issue. The most common symptom is abdominal pain, which is seen to increase or decrease in severity according to mealtimes, based on the classification of the peptic ulcer. When pain subsides after eating, the ulcer is likely duodenal, while gastric ulcers increase in pain with introduction of meals.
There are also several other symptoms including
- Bloating and fullness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Water brash
- Weight loss and loss of appetite
- Vomiting of blood
- Dark and foul feces
When ulcers are left untreated and are constantly exposed to aggravation, there can be several complications. Gastrointestinal bleeding is one of the most common complications that can be fatal if not treated. This is the typical reaction when one of the blood cells has been eroded by the ulcer.
Other complications can also present severe risk and can affect other organs within the body
- Perforation Penetration
- Scarring and swelling
- Pyloric Stenosis
Causes
For many years, ulcers have been thought to be the result of an extra spicy diet, on the job stress, and other similar factors. However, doctors have found that the true culprit of the peptic ulcer is a corkscrew shaped bacterium that is called Helicobacter pylori, or H. pylori.
This is a common bacterium that can be found within the mucous layer that lines and protects the stomach and small intestine. Although it goes through its course without disruption many times, it can sometimes disrupt this mucous layer and cause the lining of the stomach or duodenum to become inflamed, developing the ulcer.
H. pylori are commonly referred to and seen as the usual gastrointestinal infection and are thought to be spread by person to person contact or through food and water.
There are other influences, however, that can also cause these painful peptic ulcers including
- Pain killers, prescription and over-the-counter
- Smoking
- Excessive alcoholism
- Extreme stress
These influences aren’t as strong as H. pylori in causing the peptic ulcers, but can be strong contributors to the development of them due to the increase in aggravation to the stomach lining and acids. Stress can have severe effects in contributing to growth and inhibiting the healing process.
Risk Factors
The average person has a lifetime risk of 10% for actually developing a peptic ulcer. With the bacterium Helicobacter pylori being shown as the main cause for these ulcers, third world countries and areas of the world in which there are poor water and sanitation systems have a higher risk of developing ulcers.
It is also thought this bacterium infection could be transmitted through close contact and swapping of saliva during kissing, making those that are in close contact with someone prone to ulcers to also is at risk.
Smokers and those in high stress environments are also at a higher risk. The risk is also apparent for those taking NSAID medications as well.
Prevention Tips
There are some great tips you should adhere to if you want to prevent peptic ulcers from developing. As the actual cause of these ulcers is a bacterium that is hard to prevent from entering the body, you should take special precaution to avoid upsetting the stomach lining, allowing the bacterium to create an ulcer.
There are three main tips that can prevent peptic ulcer disease, that are very important to follow
Avoid smoking. If you don’t currently smoke, don’t start. If you do smoke, try finding the right way to quite as smokers have a higher risk of getting ulcers than non-smokers.
Avoid NSAIDS. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs including aspirin and ibuprofen are often taken for heart conditions, in which case a medication to prevent the stomach and intestines from irritation should be requested.
Avoid excessive consumption of alcohol. The recommended drink limit for men is 2 and women is 1, meaning that anything more could cause stomach irritation. Drinking alcohol on an empty stomach is highly discouraged as the stomach lining will have no protection from the alcohol’s effects.
Following these tips can provide a safeguard from the factors that have a strong influence on the development of peptic ulcers.
Test and Diagnosis Considerations
Peptic ulcers are quite common and with doctors knowing the true culprit, they are able to be treated most appropriately according to the cause, nature, and aggression of the ulcer. There are several different symptoms which should be monitored as there are some fatal effects of an ulcer such as stomach perforation or penetration that could cause bleeding and further complications such as anemia and even death.
When speaking to a health care professional about symptoms, it is important that the time of common occurrence, such as after meals, as well as the severity and the location where the pain is felt, is critical to the proper diagnosis of the ulcer type and course.
If it is suspected that a peptic ulcer is present, patients will undergo an EGD, esophagogastroduodenoscopy, which is a form of an endoscopy, allowing the physician to see within the stomach and inspect the stomach lining for any disruptions. For diagnosing the presence of H. pylori,
There are several different tests
- Urea breath test-eliminates the need for EGD
- EGD biopsy specimen culture-which is quite expensive
- Rapid urease test for detection of urease activity
- Antibody level measurement through blood test
- Stool antigen test
- EGD biopsy specimen histological exam and stain
Blood tests aren’t as credible as the EGD as it can be difficult for the results to tell between current infection and past exposure. There are certain medications you could have taken that can cause a false negative, allowing the ulcer to continue without appropriate treatment.
Many times, biopsies will be performed to rule out the instance of stomach cancer that could be the cause for the peptic ulcer. There is also a UGI, or upper gastrointestinal series taken, which is an x-ray of the esophagus and stomach, which can be used to distinguish the presence of peptic ulcer disease. Many physicians will also perform various other tests to identify any diseases or illnesses that may be caused by the ulcer.
Treatment Options
There are several different treatment options for peptic ulcer disease, providing relief and healing of the ulcer. These treatments vary between herbal and home remedies, prescriptions, and in the event an ulcer doesn’t respond to treatment, surgery may be required. Each of these treatments present a great relief of the ulcer and better health for the stomach lining and intestines, yet it is imperative that medications are taken as directed in order for them to remain effective.
Peptic ulcers are very debilitating and painful and can cause a decrease in the quality of life as it becomes difficult to enjoy a meal or even go out to eat. The pain can be excruciating and the after effects just as terrible. In some cases, these peptic ulcers can develop into more severe conditions that could cause severe illness and even death.
Proper identification of the ulcer and its cause is important to best be able to combat the condition and treat it properly. Without proper identification, the inappropriate medications could be used, causing unnecessary side effects and an ineffective fight against the ulcer.
Herbal and Home Remedies
There are many great herbal and home remedies suggested for the treatment of an ulcer. It is important to still seek medical advice as there may be underlying infections or illnesses that must be targeted as well. One of the most common suggestions for a home remedy of peptic ulcer disease is to use bananas. These bananas work well to neutralize the effects of the stomach acids in gastric juices. Eating two bananas each day with three to four glasses of milk is recommended for treatment of a peptic ulcer.
Another great home remedy is using almond milk that is made from blanched and blended almonds. This controls any ulcer problems and provides the body with high-quality proteins and is great in combating the excess acids in the stomach.
Fenugreek seed herbal tea is a favorite among peptic ulcer patients, coating the stomach lining avoiding the secretion of excess acids and treating the instance of an ulcer. It is important that if you are smoking, you quit properly treating and relieving the peptic ulcer.
Risks
Use of nonprescription anti-acids will provide great relief and treatment, which can be recommended by your health care provider.
The risk in herbal and home remedies and the side effects as well, are very minimal as they are organic measures that are either effective or not, but won’t cause any other effects or inhibition within the body. The effectiveness at treating peptic ulcer disease of this type of treatment isn’t as great as that with prescription and non-prescription medications, but they are effective at relieving the symptoms and promoting the healing of the ulcers.
The cost of using herbal and home remedies is much lower than other measures as most of them involve the use of a small portion of organic items.
Prescription Drugs
If the peptic ulcer is caused by H. pylori, antibiotics will be combined with either a proton pump inhibitor or a bismuth compound
- Clarithromycin
- Amoxicillin
- Tretracycline
- Metronidazole
If treatment is resisted by the ulcer and more intense means must be used, there are usually combinations of three of these antibiotics together with the proton pump inhibitor. If there is no H. pylori present, proton pump inhibitors will be used in higher doses and for a longer time.
The various antibiotic and acid suppressor or cytoprotective agent medications include
- Amoxil
- Biaxin
- Flagyl
- Helidac
- Prevpac
Each of these medications are prescribed by a physician according to the individual case and the previous occurance of an ulcer or treatment options previously pursued.
There are also acid blockers that will decrease the hydrochloric acid that is released into the digestive tract, reducing pain and speeding healing.
These medications are either provided through a prescription or over-the-counter as well
- Zantac
- Pepcid
- Tagamet
- Axid
Proton Pump Inhibitors are a great way to reduce the stomach acid release by shutting down the “pumps” that are within the acid secreting cells.
These proton pump inhiboitors include various medications such as
- Prilosec
- Prevacid
- Aciphex
- Nexium
- Protonix
Each of these medications should be discussed with a professional health care provider before use and many come with a prescription. There are various side effects when using prescription medications, as some even advise not using with an ulcer.
The side effects can include diarrhea, nausea, headache, and other more serious symptoms that should be watched for and reported if found. If there are side effects that are severe, discontinuing use of the medication may be necessary. The costs of these medications also vary and depend on the insurance and the locations these medications are purchased.
Surgery
There are cases when a peptic ulcer seems to not be affected by these medications and other therapies, requiring more extensive and aggressive measures.
The cause for the resistance to treatment by these ulcers can include many factors including
- Improper use of medications
- Resistant strain of H. pylori
- Smoking
- Excessive drinking
- Continued use of NSAID pain relievers without appropriate stomach protection
There are also some rare causes for the resistance including
- Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
- A different infection from H. pylori
- Stomach cancer
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder
When these factors are causing the most aggressive treatment measures to fail, then surgery is sometimes the only answer for relieving the ulcer and promoting treatment. This is the most expensive measure for treatment and should only be chosen if there are no effects with other treatments and medications.
There is also surgery needed if there is a malignant cancer found which is going to be very costly, but most insurance plans do cover this expense, as well as several agencies that provide assistance.
Stopping the Infection
The most appropriate treatment of a peptic ulcer is necessary to stop the infection and to increase the quality of life of which these patients experience day to day. The feeling of an ulcer each day is very debilitating and painful and could cause a stall in the activity of the patient due to the severe pain.
There are many people around the world that are afflicted by these ulcers of the various types and without proper treatment and management these ulcers can get very severe and cause long term issues and even fatality in the most extreme cases.
With ulcers so common, it is often quickly diagnosed and targeted with the most efficient manner by physicians that encounter these cases quite often. The most minor cases only require an acid blocker or antacid.
Severe Cases
The more severe cases require an antibiotic regimen of two or three combined antibiotics as well as a proton pump inhibitor to appropriately target the cause and appease the symptoms, encouraging the proper healing of the ulcer and the better health of the stomach lining and small intestines. With the stomach being a large portion of the body and a most important component, it is imperative to maintain appropriate care and treatment of any ulcers.

No Comments