Neuritis is essentially the inflammation of nerves in a specific area of the body. Neuritis causes pain and sensitivity in the affected area of nerve inflammation. A few of the most common sites in the body that tend to be frequently affected by neuritis is the eye or optic nerve, the feet and legs, alternately referred to as peripheral neuropathy. Peripheral neuropathy generally affects individuals with diabetes and multiple sclerosis.
The severity of pain associated with neuritis depends largely on the number of nerves affected as well as the location of in the body of the inflamed nerves.
Optic Neuritis
Optic Neuritis, also known as retrobulbar neuritis, is a common site for nerve pain and damage. Nerve inflammation in conjunction with optic neuritis causes pain and discomfort in the eye. When the eye moves, pain occurs due to the over-sensitivity of the optic nerve. Inflammation of the optic nerve can do more damage to the eye and vision than just discomfort. Partial or in some cases complete vision loss may occur with optic neuritis. When the nerves of the eye are inflamed, pressure tends to increase in the area behind the eye socket as well. This added pressure can cause a deterioration of the myelin sheath which acts as a protective layer coating the nerve.
Causes Of Optic Neuritis
The causes of optic neuritis vary, with the most common cause being that of an attack on the immune system which ultimately weakens and destroys the myelin sheath covering the nerve. Due to the uncertainty of why the immune system attacks itself, it is difficult to predict the underlying cause of the problem.

One of the most likely precursors of optic neuritis is multiple sclerosis. This disease unfortunately leads to vision problems in many cases. Optic neuritis and multiple sclerosis often go hand in hand. The rapid deterioration of the myelin sheath causes the nerves in the body, and in the case of optic neuritis, deteriorates the optic nerve.
Infections such as those that are of bacterial in origin, as well as lyme disease, HIV, and herpes have also been suspect as a cause for optic neuritis. A compromised immune system increases the chances of an individual developing neuritis due to the immune system being at the heart of nerve damage.
Additional Causes
Cranial arteritis is also suspect in causing optic neuritis. When the arteries supplying blood flow to the optic nerve and the eye are blocked or damaged, the chances of the nerves sustaining damage increases. Decreased blood flow can further injure an already weakened optic nerve.
Diabetes is also a common disease that increases the likelihood of optic neuritis. When the glucose levels of a diabetic remain constantly high, resulting nerve damage throughout the body, particularly in the extremities and the eyes may occur.
Certain drugs and medications are also potential causes of optic neuritis. An example of a drug that has been associated with optic neuritis as a side effect is ethambutol. Ethambutol is a medication that is frequently used in the treatment of tuberculosis.
Symptoms of Optic Neuritis
The symptoms often associated with optic neuritis are:
- Moderate to severe eye pain and discomfort
- Vision changes such as blurring or focus problems
- Loss of color vision
Very often, the symptoms of optic neuritis are indicators of multiple sclerosis. Individuals who seek medical attention for optic neuritis may subsequently be diagnosed with the condition following an examination and testing procedures.
Risk Factors Associated With Optic Neuritis
There are many risk factors associated with optic neuritis. Age is one of the risk factors of developing the disorder. As the body ages, the optic nerve tends to weaken and naturally lose some of the myelin that protects the nerves. The typical age of onset in optic neuritis is approximately 30 years.
Another risk factor involved in optic neuritis is sex. Women are two times more likely than men to develop this disorder over the course of their lives.
Race may also play a role in the likelihood of developing optic neuritis. Caucasians have a higher tendency than other races and ethnicities to develop the disease. Genetic mutations involving the optic nerve may also serve as a risk factor in this disorder.
Optic Neuritis Complications
One of the complications stemming from optic neuritis may include damage to the optic nerve which in some cases may be permanent. A decrease in visual acuity may also occur in an individual with optic neuritis. Studies indicate that up to ten percent of individuals suffering from optic neuritis will result in some amount of vision loss, usually long-term.
Diagnosis And Treatment Options
Diagnosing optic neuritis begins with a visit to an ophthalmologist who specializes in the internal disorders of the eye. The ophthalmologist may order tests such as an ophthalmoscopy in order to determine the structural soundness of the optic nerve and to detect any swelling and inflammation that may be present.
Pupillary light reaction tests may also be administered to measure the pupil’s response to light. Optic neuritis tends to damage the amount of constriction in the pupil in relation to light levels. Visually evoked potentials tests, as well as MRI scans may also be used to determine the presence of optic neuritis and the damage that may have resulted from the disorder.
A treatment option that may be employed for optic neuritis may include intravenous steroids, which helps quicken the restoration of a certain amount of visual loss that may have occurred due to the disorder. Other possible treatments include prescribing oral steroids such as prednisone may be administered. In certain cases, a procedure known as plasma exchange therapy may be of help in restoring some of the vision loss.
Peripheral Neuritis
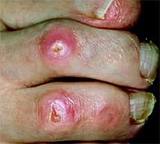
The condition known as peripheral neuritis has a direct correlation to diseases such as multiple sclerosis and diabetes. This condition is usually referred to by healthcare professionals as peripheral neuropathy. The typical complaint of peripheral neuropathy sufferers is numbness and pain in the hands and feet. The symptoms are often described as a tingling or burning sensation and a loss of feeling to varying degrees. Peripheral neuropathy usually occurs in intermittent stages. Individuals suffering with the disorder find that the symptoms appear and subsequently disappear. The severity of the neuropathy also varies greatly during its occurrence.
Causes Of Peripheral Neuritis (Neuropathy)
There are several underlying causes of peripheral neuropathy. Some of the following are typical circumstances that surround this disorder are:
- Nerve trauma due to accidents and injury
- Excessive nerve pressure such as a pinched nerve
- Vitamin and mineral deficiencies
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Diabetes
- Viral or bacterial infection
- Heavy metal poisoning
- Autoimmune disorders
- Alcohol or drug addiction
- Kidney disease
- Liver disorders
- Spinal cord tumors
Many of the causes of peripheral neuropathy are diagnosed as a result of treatment being sought for the actual symptoms of neuritis.
Peripheral Neuritis (Neuropathy) Symptoms
The symptoms often associated with peripheral neuropathy include loss of sensation in the feet and/or hands, lack of coordinating extremity movement, numbing sensations that gradually increases over time, enhancement or loss of sensitivity to heat and cold, bowel and bladder incontinence, muscular pain, and possible paralysis.
Burning and pinching sensations are also common complaints in patients with peripheral neuropathy.
Typically with the progression of the disorder, the physical symptoms may spread to the entire length of the arms and legs in some cases.
Risk Factors Of Peripheral Neuropathy
The risk factors of peripheral neuropathy are a medical history of diabetes, autoimmune disorders such as HIV, Epstein-Barr disease, lupus, and multiple sclerosis. Kidney or thyroid disease, high toxin exposure, repetitive physical trauma or accident involving the spinal cord, as well as nutritional deficiencies may also raise the risk level of developing peripheral neuropathy.
Diagnosis And Treatment
Diagnosing peripheral neuropathy will begin with a description of symptoms, blood tests, and physical examination by a healthcare professional. Nerve biopsies and MRI scans are also common diagnostic tools in determining the existence of the disorder.
The typical traditional treatment options available for peripheral neuropathy include:
- Anti-depressants
- Narcotic and non-narcotic pain medications
- Anti-seizure medications which control nerve pain
- Lidocaine patches to the affected area
Natural Cures And Remedies For Neuritis
While both optic and peripheral neuritis have their own individual treatment regimens, both are caused by aggravated nerves which may benefit from similar remedies and natural pain relievers. Some of the best home remedies that lessen the pain and discomfort associated with neuritis include some very benign products that can be obtained from a local grocery or drug store.
Much research has been done regarding the benefits of the B-vitamin family of supplements for treating both types of neuritis. Pantothenic acid, B-12, and B-2 are essential in protecting and optimizing nerve function. Another popular home remedy that is helpful in the reduction of nerve pain is carrot and spinach juice. The vitamins and minerals found in both of the vegetables provide excellent antioxidant support for the nerve and the body as a whole.
Barley Brew
Barley brew is also a potent pain reliever in response to neuritis. Boiling the barley brew and mixing it with buttermilk and lime juice make for a tasty home remedy. Beet juice is also a wonderful vegetable that is filled with many essential vitamins that help promote healing and nerve restoration.
Epsom Salt
A proven remedy for neuritis flareups is the epsom salt bath. Epsom salt baths should be taken three times per week in order to calm aggravated nerves and relieve pain and discomfort associated with neuritis. An effective means of gaining strength and building up bodily endurance during neuritis flareups is exercise. Soya bean milk is another home remedy used in treating neuritis. The natural chemicals found in soya beans help improve nerve function and should be taken once daily, preferably at night before bed.
Exercise
While most people who suffer from this disorder would cringe at the thought of exercise during such bouts of neuritis, moving the body by moderate walking for twenty minutes per day can help lessen nerve pain. Mild to moderate physical activity helps strengthen the body and muscles and relieves discomfort due to the natural hormones that are released by the body during exercise. Proper stretching should be done before and after any exercise routine, even if the exercise is light. This is necessary in order to avoid muscle strain or injury which would only heighten the problems with neuritis.
Things To Avoid During A Neuritis Flareup
There are several things that sufferers of neuritis should avoid in order to lessen pain and discomfort as well as promote speedy healing. Cut back on or avoid the following items:
- Canned meats such as tuna and salted fish
- White refined breads and cereals
- Coffee
- Tea
- Caffeine products
The above items will only add to the complications of neuritis and should be avoided if all possible during a bout with neuritis.
Neuritis can be a debilitating illness that causes nerve pain and discomfort for sufferers. With the proper treatments, both with traditional and natural remedies, a pain free life may be enjoyed once again.