Jaundice is a yellowish discoloration of the pigment in the skin that results in several other problems as well. The condition is most commonly found in newborns and infants but can affect adults as well. The term “Jaundice” comes from the French language and means “yellow”.
Alternative Names For Jaundice
The most common alternative name for jaundice is Icterus. Other terms are Yellow Skin and Yellow Eyes. There are also several different types of jaundice, each of which is given a distinct name. Neonatal Jaundice is the most common form and occurs in newborns a few days following birth. Hemolytic Jaundice is caused by the body’s red blood cells being destroyed or broken down. Hepatocellular Jaundice is the result of a dysfunctional liver, or a liver that is unable to properly produce bilirubin.
These are the most common types of jaundice but other rare forms may exist and have only been rarely documented.
Symptoms That May Accompany Jaundice
The most common symptoms of jaundice are a slight yellowing of the skin and a similar yellowing in the eyes. For most infants, parents will first notice the discoloration in their baby’s face. The yellowing will continue downward beginning in the chest and then falling towards the arms, stomach, and legs. Infants may also experience some of the following symptoms as well:
- High-pitched or drawn out screams.
- The infant may always seem sick, sleepy, and difficult to wake up.
- Slow-weight gain.
- Other signs such as irregular bowel movements and a high fever.
Adults will have similar symptoms as an infant when dealing with jaundice, but may also notice a few other signs. Jaundice will often be accompanied by the urine becoming a brown-yellowish color. Stools may become more pale or white in adults who have jaundice. Because jaundice denotes to there being a problem in the liver and digestive system, the person may also experience vomiting, diarrhea, nausea, and a loss of appetite.
Causes Of Jaundice
Jaundice is typically the result of too much bilirubin being produced so that the liver cannot remove it from the bloodstream. Hemoglobin is a chemical which is found within all red blood cells and is beneficial to the survival of the cells. When red blood cells become old or not useful, the body will destroy them and release the iron that is found within the Hemoglobin. Bilirubin is produced as the product of the iron being released from the Hemoglobin. If too many red blood cells are dying and too much bilirubin is being produced, the body may not be fully capable of dealing with so much bilirubin.
Jaundice? Get Remedies Fast!
The production of too much bilirubin may not always be the culprit. Often times the liver will have a small defect that prevents the bilirubin from being removed from the blood. Other times a blockage may arise within the digestive system that blocks the flow of bile and bilirubin tot he intestines. This will cause less flow of the bile and can result in a form of jaundice that is related to a disease called cholestasis.
In the case of infants, jaundice is caused by a slightly different problem. A newborn infant will have a very high amount of red blood cells whose life cycles are relatively short. Because of this high turnover rate of red blood cells, infants may have excess bilirubin during the first few weeks of life. Other causes of jaundice in newborns can include:
- Some type of internal bleeding or hemorrhage.
- A blood infection.
- Some viral and bacterial infections can cause the skin to turn yellow, similar to jaundice.
- A dysfunctional or malfunctioning liver
- Some form of abnormality in the infant’s red blood cells.
The term jaundice refers to the actual “yellowing” of the skin and eyes, but is not a disorder in itself. Jaundice is typically a sign that there may be a problem in the liver or digestive system.
Risk Factors That Can Be Related To Jaundice
Premature infants are at the greatest risk of having jaundice. Babies born before 37 weeks are among those with the highest risk of having jaundice. Infants born after 37 weeks may still have jaundice but are at less of a risk. The reason that prematurely born infants have a greater risk of jaundice is due to the liver being less developed.
Babies who are born with a blood-group incompatibility are also at risk. Incompatibilities issues arise if your baby has a different blood type than your own. Babies who receive intense bruising during birth may have a higher level of bilirubin in their body due to the destruction of more red blood cells. Thus, bruised babies may have a greater chance of having jaundice. Children who are breast-fed have a higher risk of jaundice, especially if they are having a difficult time nursing and are not receiving the proper amounts of nutrition.
In the case of adults, those who have had some form of Hepatitis are generally at the greatest risk. Also, people who have alcoholic liver diseases or are heavy drinkers are at a risk of jaundice. Persons infected with the HIV virus or other sexually transmitted diseases may be more susceptible to having jaundice. The recipient or donor of a recent liver transplant or other operation on the liver may also show signs of jaundice.
Prevention Tips To Help Avoid Jaundice
Because jaundice occurs in over 75% of newborns, it can be difficult to prevent. While in the womb, the baby relies on the mother’s liver to perform most of the reduction in excess bilirubin. When the baby is born his or her liver may not yet have had the practice to do this on their own. With time their own livers will be able to remove excess bilirubin.
The best way to prevent jaundice from becoming more sever is to ensure that your infant is getting the nutrients he or she needs by properly breast feeding them. Infants should be fed 8 to 12 times a day on average and be fed approximately every two hours.
Children should be examined within 5 days of birth by a trained children’s physician. The child’s doctor may be able to note signs that suggest jaundice before the parents can and thus prevent the jaundice from becoming worse. Also, make sure to check your infant’s urine and stool. Urine should be odorless and clear, if it is a yellowish color then that may be a sign of jaundice. A stool that is pale, pink, or purple may be accompanied by jaundice. Healthy stools range in color from green to yellow.
Adults can prevent jaundice by avoiding those activities which may be related to some of the above mentioned risk factors. Adults who drink excessive alcohol and contract liver disease may have jaundice. One of the best ways to prevent jaundice in adults is to avoid alcohol. Adults should also avoid any sexual activity, such as unprotected sex, that may put them at risk of a sexual disease. Do not allow yourself to be poked by an unclean needle. If you have recently had an operation that has affected your liver it is important to follow all of the surgeon’s advice in order to care for your liver and prevent jaundice.
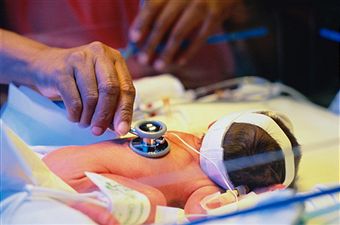
Tests And Other Diagnosis Considerations When Dealing With Jaundice
Infants will commonly receive blood and urine tests that can determine whether or not they have jaundice. The most common test is called the “Bilirubin Test”. The Bilirubin Test is simply a test of the blood to determine if bilirubin levels are too high.
Adults who take this test should not eat or drink for 4 hours prior to appointment. Levels of bilirubin in the blood is typically between .20 mg/dL to 1.5 mg/dL, anything that is significantly higher than these amounts should require a physician’s attention
Adults who have signs of jaundice that may denote a more severe health problem may be more fully examined with the aid of ultrasound techniques, CT and MRI scans, or an endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. These scans are used to examine organs, such as the liver, and determine any malfunction.
The scans can also be used to uncover any blockages near the liver that are preventing excess bilirubin from exiting the body. A liver biopsy, in which a small piece of liver tissue is extracted and examined, may also be used in order to determine if the liver is not performing its proper function.
Treatment Options
Herbal And Home Remedies Commonly Used To Treat Jaundice
Several herbs have been used for hundreds of years to help buildup a strong liver. These herbs can also help fight against jaundice, but should be used accompanied by medical care and not by themselves. Some commonly used herbs include:
- Bitter Luffa
- Radish Leaves
- Tomatoes
- Snake Gourd Leaves
- Pigeon Pea Leaves
- Sugarcane Juice
- Lemon Juice
- Barley Water
- Jaundice Berry (also known as Berberis vultaris)
Most of these herbs can be found at a local Herbologist’s or Naturalist’s office, and some can be found at general nutrition centers and department stores.
Proper home care of jaundice is best provided by receiving adequate physical rest. Recovery is dependent upon the liver being able to handle the amount of bilirubin from destroyed blood cells. Blood cells are destroyed less when a person is sleeping or resting than when they are physically active. Patients should drink plenty of juice of all kinds throughout the day and be on a light carbohydrate diet..
Pharmaceutical Treatments Of Jaundice
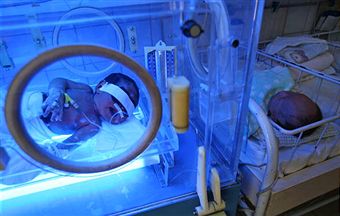
Infants who have severe jaundice will often be recommended to use phototherapy. Phototherapy is the use of light waves to eliminate excess bilirubin in your baby’s blood. The skin and blood will absorb certain light waves and can use the energy of the light to change the bilirubin into more useful products that their body can either use or pass through their digestive system. Phototherapy is relatively inexpensive and special “biliblankets” can be used at home in order to avoid excess hospital bills. Phototherapy can often cause frequent or loose bowel movements, but this is normal. If these bowel movements persist for an extended period of time following the treatment of jaundice you should contact a physician.
Because jaundice in adults is usually related to some other disorder or disease, physicians will typically not prescribe antibiotics or other medications unless they are used to cure the related disorder.
Surgical Treatments For Jaundice
Gall stones can often be the cause of jaundice in adults. In this case, a surgeon may opt to remove the gallstone and remove any excess bile from the patient. Blood transfusions can be performed on infants and adults who experience sever jaundice. Aside from these cases, surgery is not necessary in the treatment of jaundice. In the case of a sever liver problem that is also accompanied by jaundice, the patient may be required to have a liver transplant.

No Comments