Overview of Morning Sickness
Morning sickness is a condition which occurs during pregnancy that affects approximately more than half of all pregnant women, but it may also be experienced by women using hormonal contraception or hormone replacement therapy. Usually prominent during the early hours of the morning, morning sickness can occur during any part of the day including during the night.

This condition may be experienced only as mild nausea, or it may cause actual vomiting. In only about 1% of all pregnancies, vomiting may become severe enough to cause dehydration, weight loss, alkalosis (a condition in which the pH of the blood is elevated beyond normal and results in hypoventilation as an attempt to balance the pH), and hypokalemia (a condition in which the concentration of potassium (K+) in the blood is low which may result in elevated blood pressure, cardiac arrhythmias, and/or muscle weakness); this severe form of morning sickness is known as hyperemesis gravidarum.
Morning sickness may be one of the earliest signs that a woman may be expecting a child and usually begins around the 6th week of pregnancy, and it seems to cease around the 12th week of pregnancy for most pregnant women which marks the end of the first trimester and the beginning of the second trimester of pregnancy. However, morning sickness may continue throughout the entire pregnancy for some women.
Alternative names of Morning Sickness
- Nausea gravidarum
- Nausea
- Vomiting of pregnancy
- Emesis gravidarum
- NVP
- Pregnancy sickness
Symptoms of Morning Sickness
Nausea during pregnancy which may or may not be accompanied by vomiting.
Causes of Morning Sickness
- Some women are sensitive to the hundredfold increase in the hormone estrogen circulating in their blood.
- Progesterone also increases which relaxes the smooth muscles of the uterus as well as the smooth muscles of the stomach and intestines resulting in excessive amounts of stomach acids which leads to heartburn, or gastrointestinal reflux.
- Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, may be to blame for nausea and/or vomiting in pregnancy due to the placenta taking energy from the expectant mother.
- A sudden increase in the pregnancy hormone, HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin), may inevitably cause nausea.
- Increases in the hormone cholecystokinin causes slowed digestion in order for more efficient nutrient absorption to take place both for the mother as well as the growing fetus.
- Perhaps as a built-in defense mechanism against harmful substances, pregnant women tend to experience an increase in sensitivity to odors, which therefore over stimulates the nausea center of the brain.
Risk Factors of Morning Sickness
- A pregnant woman may be at risk for pregnancy-related nausea if she has ever experienced any of the following prior to the current pregnancy: motion sickness, migraines, sensitivity to certain smells or tastes, sensitivity to estrogen in birth control pills, or she has experienced morning sickness during a previous pregnancy
- An expectant woman may also be at risk for morning sickness if she is pregnant with more than one fetus.
Complications of Morning Sickness
Complications that could jeopardize the pregnancy may arise as a result of more severe morning sickness, hyperemesis gravidarum, and include the following:
- Dehydration
- Malnutrition
- Weight loss
- Alkalosis
- Hypokalemia
- Acid reflux
- High blood pressure
- Hypoventilation
- Muscle weakness
- Cardiac arrhythmias
Tips for lessening nausea and avoiding vomiting associated with morning sickness:
- Consume foods that are high in carbs but low in fat.
- Salty foods such as pickles, pretzels, and saltines as well as foods containing ginger can help in lessening and/or preventing morning sickness.
- Avoid greasy, spicy and fatty foods which help create more stomach acid.
- Eat six small meals rather than three large meals per day.
- Have some saltines handy on your nightstand to nibble on 15 minutes before getting out of bed in the morning.
- Avoid an empty stomach which may aggravate nausea.
- Drink water and other liquids 30-45 minutes before or after meals.
- Sip water and/or ginger ale throughout the day to avoid an empty stomach and/or dehydration.
- Sucking on something hard such as candy or ice chips or ice pops may be helpful.
- Avoid known nausea triggers such as foods or smells that seem to aggravate your nausea.
- Expose yourself to as much fresh air as possible versus stale indoor air.
- Take your prenatal vitamins at night with a snack to avoid queasiness brought on by the vitamins.
- Expose yourself to the smell of freshly cut citrus fruits such as lemons.
- Accommodate food cravings (things you want) and aversions (things that aggravate your morning sickness) when possible.
- Pregnant women tend to crave or get nauseated by things typically because their bodies are telling them what they need or what they need to avoid in order to have a healthy pregnancy outcome.
- Consume fruits and vegetables with a high water concentration such as tomatoes, melons, citrus fruits, strawberries, leafy vegetables, and grapes.
- Try the BRATT diet to keep your stomach settled. The BRATT diet is simply made up of bananas, rice, applesauce, toast and tea.
- If the smell of food being cooked aggravates your nausea, have a loved one cook for you, and make sure there is plenty of ventilation such as having a fan on and/or windows open.
- Rest as often as humanly possible!
- Avoid getting overheated which exacerbates pregnancy nausea.
- Try to work in some light exercise such as walking and/or swimming, but don’t over do it.
- Avoid laying down immediately after eating. Try to allow 2-3 hours after eating to avoid stomach upset caused from acid.
Testing and diagnosis for Morning Sickness
There are no specific tests available to diagnosis morning sickness in itself due to the fact that morning sickness is merely a symptom of pregnancy. On that note, a positive pregnancy test may tell a woman the cause of the nausea and/or vomiting she has been experiencing.
However, sever morning sickness known as hyperemesis gravidarum, or HEG, may require further testing in order to rule out other complications in the pregnancy.
Further testing may include the following:
- Amylase
- Blood calcium level
- Serum electrolytes, which can show low potassium or sodium levels in blood. Low levels can mean dehydration or acid-base imbalance.
- Hematocrit, part of a blood count, which may become high due to dehydration
- Liver enzymes and bilirubin
- Urinalysis for ketones and specific gravity. Ketones are a sign of starvation. Specific gravity can show dehydration.
- An ultrasound may also be done to check the condition of the baby and the womb.
- If a woman has abdominal pain or vomits blood, the doctor may do an endoscopy. This is a test where a small tube is passed through a woman’s mouth and throat down to her stomach. The tube has a light at the end, which helps the doctor to look for problems in the stomach.
- Serum for hepatitis testing
- Liver function tests
- Ultrasound to look at gallbladder
- Urinalysis and culture to test for bacteria
- Ultrasound to look for twins or a tumorous growth of the placenta
Treatment Options for Morning Sickness
Herbal & Home Remedies
- Drink a few teaspoons of wheat germ dissolved in warm milk every hour until the nausea subsides.
- Take 1 tablespoon of apple cider vinegar mixed with 1 tablespoon of honey in cold water before bed.
- Suck a piece of peeled ginger root.
- Drink red raspberry leaf tea.
- Drink peppermint or spearmint tea.
- Drink squaw vine tea.
- Drink ginger tea. Make the tea by boiling some ginger root in water then straining it. Finally, add honey to taste.
- Rear motion sickness bands on your wrists where pressure points which control nausea are located.
- Put three drops of lavender essential oil and one of peppermint in a diffuser or humidifier to scent the air.
- Place a cool lavender scented compress on your forehead and a warm lavender compress over your rib cage.
- Have a loved one massage you with a soothing chamomile massage oil.
- Snack on ginger snap cookies made with real ginger.
Pharmaceutical Remedies
Non-prescription morning sickness remedies include the following:
- Emetrol is the only non-prescription nausea medication that’s considered safe during pregnancy.
- For women whose nausea and vomiting is triggered by acid, reflux medications such as Zantac or Pepcid may work.
- According to the FDA, the combination of Doxylamine and vitamin B6 is considered safe and effective for nausea and vomiting associated with pregnancy.
- Doxylamine is available as a sleeping pill under the brand name Unisom Nighttime Sleep-Aid, not Maximum Strength Unisom Sleep Gels which is an entirely different product. Vitamin B6 may be located in the vitamin section of your local grocery store or pharmacy.
Prescription Remedies
Compazine
Possible side effects:
- Abnormal muscle rigidity
- secretion of milk
- sugar in urine
- abnormalities of posture and movement
- agitation
- anemia
- appetite changes
- asthma
- blurred vision
- constipation
- convulsions
- difficulty swallowing
- discolored skin tone
- dizziness
- drooling
- drowsiness
- dry mouth
- exaggerated reflexes
- fever
You should never suddenly stop taking Compazine, due to adverse effects such as a change in appetite, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and tremors. When discontinuing this drug, it is important to follow your doctor’s instructions closely. Your ability to drive a car or operate heavy machinery may be impaired when taking this drug, so take extreme caution when participating in any activities that require full alertness. Take caution when outdoors due to sunlight sensitivity related to the use of Compazine. Avoid direct sunlight and use sun block and wear protective clothing including sunglasses. Also, beware that Compazine may interfere with your ability to shed extra heat, so take caution in hot weather.

Be sure your doctor is aware of any drug you are taking. Compazine may interact with the following drugs: Anti-seizure drugs such as Dilantin and Tegretol, Anticoagulants such as Coumadin, Guanethidine (Ismelin), Lithium (Lithobid, Eskalith), Narcotic painkillers such as Demerol and Tylenol
with Codeine, Central nervous system depressants such as Xanax, Valium, Seconal, and Halcion Propranolol, and Thiazide diuretics such as Dyazide
Tigan
Possible side effects:
- Hypersensitivity reactions
- Parkinson’s-like symptoms
- blood dyscrasias
- blurred vision
- coma
- convulsions
- depression of mood
- diarrhea
- disorientation
- dizziness
- drowsiness
- headache
- jaundice
- muscle cramps
Tigan is contraindicated and should not be used in patients with known hypersensitivity to trimethobenzamide. Stop using this drug and tell your doctor immediately if any of these serious side effects occur.
Conclusion
Once more, morning sickness may range anywhere from mild nausea to severe vomiting. Before using any remedy, whether it be a herbal/home remedy or a medication, always first consult with your physician. Home remedies should be your first line of defense for morning sickness due to adverse effects related to the use of medications. If all else fails, your doctor can help you decide on the best treatment option for your morning sickness. Remember, the healthier Mom is the healthier the baby will be!



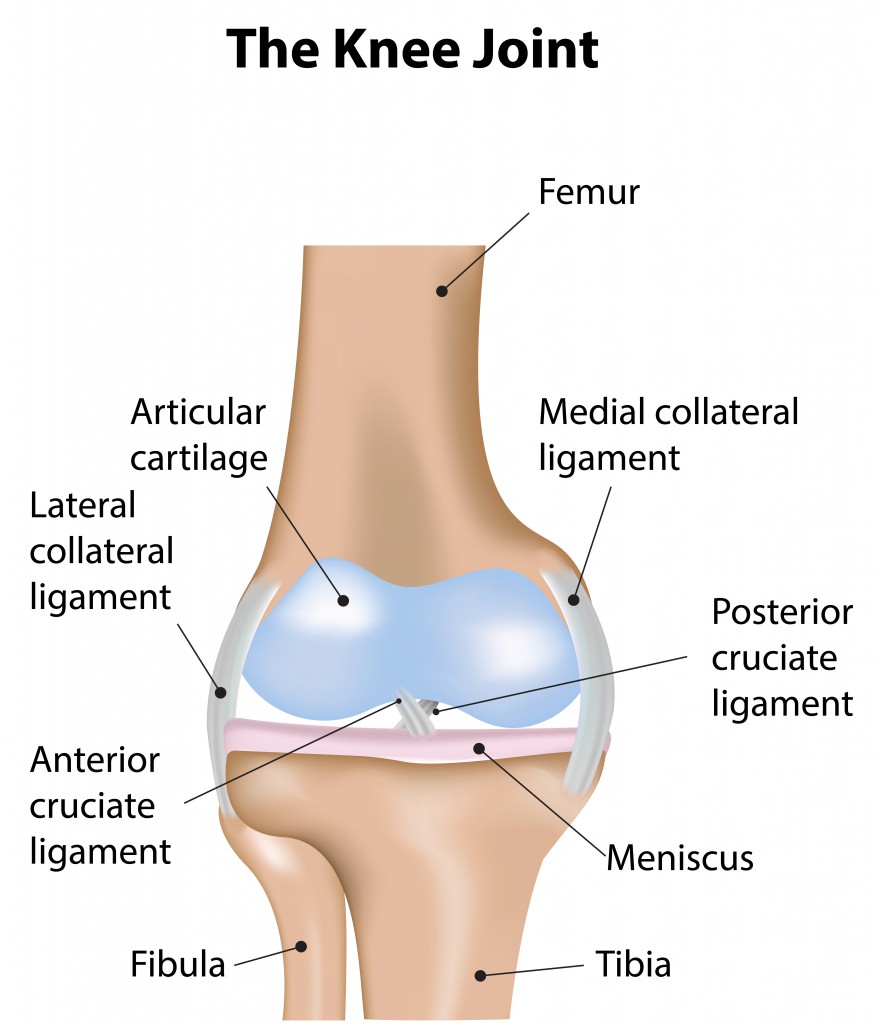
 Whether recovering from a knee injury or just trying to avoid knee injury and pain altogether, knee strengthening exercises are a great solution. Also, wear proper shoes with an adequate amount of foot support. If one is involved in a heavy exercise workout or knee-demanding sports such as basketball or skiing, be sure to warm up with stretches before engaging in such activities.
Whether recovering from a knee injury or just trying to avoid knee injury and pain altogether, knee strengthening exercises are a great solution. Also, wear proper shoes with an adequate amount of foot support. If one is involved in a heavy exercise workout or knee-demanding sports such as basketball or skiing, be sure to warm up with stretches before engaging in such activities.