Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a disorder that has multiple symptoms affecting the abdomen and intestinal tract. IBS has been called a functional disorder in that those diagnosed with the illness have symptoms of disease, but the colon and intestines show little indication of anything abnormal. This creates frustration for those suffering from the pain and stool changes associated with the disorder and with those who must alter their lives in order to manage the illness.

Alternative Names for Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome has often been misunderstood as an illness, and is frequently diagnosed when other bowel diseases have been ruled out.
Historically, IBS was associated as being symptomatic of mental instability, as patients would present with abdominal symptoms, but the bowel remained intact without signs of disease.
Because of this, the condition used to be labeled as “nervous bowel,” in that physicians attributed the physical symptoms to a nervous disorder. IBS is now understood to be a physical condition that affects millions of people in the United States.
Irritable bowel syndrome has also been called irritable colon, or spastic colon. This may be related to findings of changes in the motility of the large intestine. This causes the symptoms associated with the illness, yet no inflammation is found to be associated with the colon.
Physicians believe the colon alters its own patterns of movement as it transfers waste through the body toward the rectum. IBS has often been confused with other diseases or has been inaccurately labeled as colitis, diverticulitis, or Crohn’s disease. All of these diagnoses are separate illnesses that show bowel changes or disease processes that are related to symptoms and are not the same as irritable bowel syndrome.
Symptoms Related to the Illness
The symptoms associated with irritable bowel syndrome are related to the abdomen and large intestine. Symptoms may last for days or weeks, followed by a period of normal bowel activity, only to reappear again at another time. This creates a chronic condition for the suffering patient, who may not seek immediate treatment, as they may believe each time that the symptoms will not recur.
Symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome can include a combination of any of the following
- Abdominal pain
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Bloating
- Flatulence
- Fatigue
Abdominal pain is a common symptom associated with irritable bowel syndrome and is frequently described as abdominal cramps. The abdomen may feel sensitive to touch or the pain may be localized to a specific area. Pain is frequently relieved after having a bowel movement.
Diarrhea & Chronic Diarrhea
Diarrhea is the most frequent complaint by those suffering from irritable bowel syndrome. Diarrhea is considered the passing of loose, watery stools.
With IBS, there may also be mucous noted in the stool. The diarrhea can occur for several days or even weeks at a time, and typically develops after eating a meal. This causes discomfort and embarrassment for the affected person. The patient with IBS may feel isolated or trapped in that they are unable to eat a meal away from home if their destination does not have a bathroom available.
Chronic diarrhea can cause dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, and skin breakdown near the rectum. Patients diagnosed with IBS who suffer from frequent diarrhea must monitor their food and fluid intake and may need medication to slow their motility. Diarrhea that is bloody is not considered a symptom of IBS and is indicative of a more serious illness.
Constipation
Patients with irritable bowel syndrome may alternate between having diarrhea and constipation. Constipation is the presence of hard stools that are difficult to pass. It may cause abdominal pain, bloating, or the sensation of pressure associated with needing to have a bowel movement. A patient with IBS may suffer from diarrhea for days or weeks, followed by a period of constipation for a similar timeframe.
Bloating may be associated with constipation in irritable bowel syndrome, or it may appear as an isolated symptom of the disorder. Bloating is the feeling of fullness in the abdomen, causing discomfort. A person may feel awkward with movement or that clothing is tight. Bloating may also lead to belching as a means of expelling excess air in the stomach.
Flatulence
Flatulence is the passing of gas through the rectum and is frequently associated with irritable bowel syndrome. Flatulence may also be associated with bloating or abdominal pain. The pain is then relieved for the patient by passing gas. Flatulence creates feelings of embarrassment for patient diagnosed with IBS, and they may avoid certain social situations until symptoms are controlled.
A person diagnosed with irritable bowel syndrome may have fatigue and a lack of motivation. Fatigue can be the result of the body managing symptoms of illness over an extended period of time. For the person suffering from IBS, the symptoms of chronic diarrhea, bloating, and abdominal pain can all cause fatigue.
Anxiety and Depression
Many patients with irritable bowel syndrome also report feelings of anxiety and depression. Anxiety can occur because symptoms of IBS may be unpredictable. A patient may feel uncomfortable in social situations due to their symptoms, or they may need to know if there is a bathroom readily available if necessary. Depression results from the management of chronic symptoms.
Some patients do not seek treatment right away, believing the symptoms will go away on their own. Or, they may have seen a doctor that could not find anything physically wrong with the bowel, leaving them to believe they might be imagining their symptoms. Depression and anxiety are the emotional consequences of IBS and may be difficult for the patient to manage.
Causes of Irritable Bowel Syndrome
The exact cause of irritable bowel syndrome is unknown. Experts have attributed the symptoms to stress, food intolerance, or other illness, but a specific cause has yet to be defined. Because of this, diagnosis and treatment of IBS can be difficult.
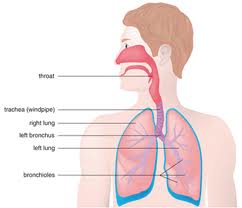
During digestion, food that is eaten travels from the mouth and through the esophagus, which is the narrow tube that leads to the stomach. After passing through the stomach, food enters the small intestine where it continues to break down with the help of enzymes from the liver and where nutrients are absorbed. The leftover products of digestion enter the large intestine, or the colon, and are eventually passed from the body through the rectum.
With symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome, it is thought that changes may take place during some parts of this process of digestion. The colon may develop a spastic pattern of movement, resulting in bowel changes. There may be an alteration in the amount of fluid that is absorbed by the body, producing constipation or diarrhea.
Some foods react with the body to produce gas molecules during digestion, which creates bloating and flatulence. Irritable bowel syndrome may be caused by one or a combination of these factors. Despite the obvious symptoms, physicians otherwise do not find inflammation, stricture, or any other indications of disease when examining the colon. This is why IBS is a diagnosis of exclusion: the patient suffers symptoms without an exact cause.
Risk Factors for Irritable Bowel Syndrome

Irritable bowel syndrome affects women twice as many times as men, and experts have considered hormonal changes as a possible cause of symptoms.
For this reason, women are at higher risk than men of developing the disorder.
Young adults are also affected more commonly with IBS than children or those that are middle-aged.
Because the exact cause of the disorder is unknown, risk factors can be otherwise difficult to determine.
Persons that experience large amounts of stress in their lives may be at risk for developing IBS and its associated symptoms, due to the physiological response that stress can create in the gastrointestinal system.
Some people do not tolerate certain foods, or develop symptoms of IBS after eating meals and so become at risk for abdominal issues.
Patients that have undergone treatment for medical illness are also at greater risk of developing IBS.
The connection between medical treatment and IBS is thought to be related to infection of the gastrointestinal tract that causes symptoms but does not show major damage to the colon.
Experts are still researching the relationship between infection and IBS.
Prevention of the Illness
There is no cure for irritable bowel syndrome, but its symptoms may be managed in a method that reduces them almost entirely. For a person who is exhibiting signs of IBS, there are several preventative measures that may be taken to avoid the recurrence of many symptoms.
A stressful lifestyle may induce or exacerbate symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome. Patients should manage the amounts of stress in their lives and make lifestyle changes if necessary to avoid high-pressure situations or chronically stressful living. Participating in activities that are enjoyable or exercising frequently reduces stress levels and can have a positive impact toward feelings of anxiety and depression if they appear.
Monitoring food intake to determine if certain foods cause reactions is a proactive approach to managing IBS. Some foods, such as broccoli or beans, can cause excess gas, which contributes to bloating and flatulence. Excessive alcohol can negatively impact the body and should be avoided. Foods and drinks such as prunes, apple juice, or other types of fruits that can increase motility should also be avoided to reduce the occurrence of diarrhea.
Diagnosis of Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome is frequently seen in the offices of general practitioners and gastrointestinal specialists. It is diagnosed in approximately one-third of office visits related to abdominal symptoms. IBS is a diagnosis of exclusion, in that the patient presents with symptoms that cannot be attributed to any obvious source.
Other gastrointestinal illnesses, such as celiac disease, diverticulitis, or colitis can be diagnosed through testing. Many patients undergo testing and procedures only for the physician to find no obvious results.
Diagnosis of IBS is made after a physician has tested the patient for other diseases with little results. A physician may order lab testing of the blood to determine if the patient has electrolyte imbalance or infection. A stool test may be ordered to check for microscopic blood or bacteria.
Testing
A physician may take a full history to determine the patient’s symptoms, how often they are occurring, and if there is any family history of gastrointestinal disease. They may ask questions about the patient’s lifestyle, such as food intolerances, alcohol consumption, smoking habits, and allergies.
A physician may order other tests that are specific to the intestinal tract to look for signs of inflammation or disease. A barium enema is a test that allows a physician to look at the motility of the patient’s colon. The patient is given a dose of barium, which is a substance that, when ingested, appears during an x-ray. The barium is administered into the rectum of the patient and an x-ray of the bowel can be seen. A physician can then take radiologic images of the bowel to watch the patient’s motility
Colonoscopy
Another test that may be administered to look for abdominal disease is a colonoscopy, although it is considered a relatively invasive course of action and may not be necessary in all cases. A colonoscopy is a procedure that is indicated for diagnosing an inflammatory disease process in the bowel, which may present in a mode similar to irritable bowel syndrome.
The patient is given a laxative to take before the procedure in order to empty the colon. A sedative is given to the patient to help with relaxation during the procedure. The doctor inserts a flexible tube with a small camera on the end into the patient’s rectum and advances it to visualize the colon.
The procedure will show areas of inflammation, polyps, or strictures. If there are no indications of disease, a diagnosis of irritable bowel syndrome may be made by the process of exclusion.
Treatment Options for the Disorder
Treatment of irritable bowel syndrome is aimed at managing symptoms of the disease. While not life-threatening, IBS forces patients that are diagnosed to alter their lifestyle to manage symptoms when they occur. Treating symptoms as they occur or utilizing prevention tips can vastly diminish the incidence of symptoms.
Abdominal pain is often associated with intestinal cramping related to diarrhea or constipation. Treating either of these symptoms can reduce the amount of abdominal pain the patient may be experiencing. Diarrhea can be managed by avoiding foods that have a laxative effect, such as certain fruits or seeds. Over the counter medications that help slow motility can reduce diarrhea if it is recurring. Patients should also drink plenty of water to reduce the possibility of dehydration.
High Fiber Foods & Exercise
Alternatively, constipation can be relieved by eating foods that provide a laxative effect, as well as high fiber foods to promote regularity. Some fiber supplements can be mixed with food or drink as part of a meal. Severe constipation may be relieved with a stool softener, which can be purchased over the counter or prescribed by a physician. Avoiding foods that produce excess gas and bloating, such as cabbage or lentils; dairy products; or carbonated beverages can reduce the amount of discomfort associated with these symptoms.
For those patients suffering from fatigue, anxiety, or depression related to their diagnosis, a blend of exercise and frequent rest may help with some negative emotions and lack of energy. For severe feelings of distress, a doctor may prescribe medication to cope with difficult emotions and to help the patient accept the terms of their disorder.
Irritable bowel syndrome is more common than many people realize, and has become one of the most frequently diagnosed gastrointestinal conditions in the United States. Although symptoms can be inconvenient and difficult to manage, IBS is not considered a major medical condition. With proper prevention and management of symptoms, IBS can be successfully controlled and suffering persons can take back their lives.