Low blood sugar, or hypoglycemia, occurs when blood glucose (sugar) levels fall to abnormal levels. Most doctors define low glucose levels below 70 ml/dl on a glucose meter, although symptoms don’t usually appear until levels fall below 60 ml/dl. (If levels fall below 50 ml/dl brain function is greatly affected.) A glucose reading only takes a small drop of blood and is quick procedure that can be performed at the doctor’s office or with a home glucose meter.
Low blood sugar may also be known as insulin reaction, diabetes mellitus, or adrenal insufficiency.
What Causes Low Blood Sugar?
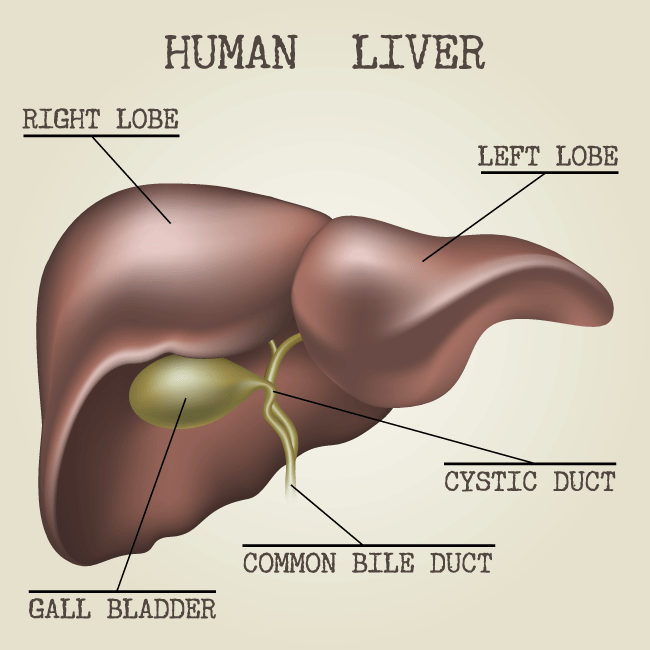
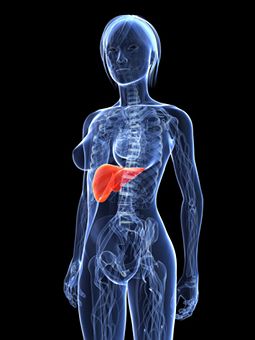
Low blood sugar happens when the body is unable to properly process large amounts of sugar in the blood stream. The pancreas, an organ near the stomach, secrets the hormone insulin in response to a spike in sugar levels, and if the pancreas secrets too much insulin, the hormone will not only deplete the excess sugar, but it will eat into the normal levels as well, robbing the body’s cells of fuel.
Insulin facilitates the transport of glucose through the bloodstream to muscle, fatty tissue, and brain cells, and causes the glucose to be synthesized by the liver.
All cells, especially brain cells, need glucose to function properly. If the brain does not have enough glucose to function properly, it will eventually shut down.
Most of the time low blood sugar is seen in people with diabetes who take regular insulin.
If insulin levels are not properly regulated, sugar levels can easily plummet. In rare cases hypoglycemia is the result of a malfunctioning pancreas or the result of liver disease.
Somewhat ironically, problems with low sugar are often an early indication of the onset of diabetes (high blood sugar).
It can also occur with the use of medications such as beta blockers, pentamidine, and sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprin.
Other disorders can contribute to the occurrence of low blood sugar, including:
- Thyroid disorder
- Adrenal insufficiency
- Pituitary disorder
- Pancreatitis
- Kidney disease
- Liver disease
- Liver tumor
- Pancreatic tumor
In American culture low blood sugar is often a result of too much simple sugars, alcohol, tobacco, caffeine and stress. Carbohydrates (found in grains, sugars, fruits and vegetables as well as white table sugar) are broken down into simple sugars in the digestive system. The sugar is converted to glucose and enters the bloodstream to serve as fuel for the body. The pancreas then secretes insulin to regulate sugar levels. Large amounts of carbohydrates will cause blood glucose levels to rise quickly, causing higher insulin levels to compensate. Although hypoglycemia can be inherited, it is most often a result of a poor diet. This type of low blood sugar condition is referred to as functional hypoglycemia, and is fairly common although rarely diagnosed.
Low blood sugar can also occur with high levels of stress. When a person is stressed, the body releases adrenalin which causes the body to release stored glucose levels. This process happens to provide the body with needed fuel during a stressful situation. However, if those stores are not used by physical activity, the pancreas then secrets insulin to bring down the higher levels of glucose in the blood. The body is now deficient in glucose stores, and symptoms of hypoglycemia may become apparent. Maintaining a highly-stressful lifestyle increases the possibility of recurrent low blood sugar issues.
In other cultures, where diets do not contain high amounts of sweeteners (which easily convert into sugar) hypoglycemia is rarely seen as a byproduct of diet. In poorer economies, although the typical diet may contain high amounts of carbohydrates, the people generally eat smaller portions and burn carbohydrate sugar levels though physical labor.
Symptoms of Low Blood Sugar
An early sign of low blood sugar often manifests as a craving for sweets and starches between meals. If glucose levels get too low, more pronounced symptoms may occur including:
- Trembling
- Numbness
- Nausea
- Blurred vision
- Headache
- Pain in the eyes
- Dizziness
- Insomnia
- Irritability
- Fatigue
- Heart palpations
- Weakness
- Rapid heart beats
- Sweating
- Anxiety
The body begins to respond to hypoglycemia when blood sugar levels reach 70 ml/dl, although you may not notice symptoms at this time. Insulin production also decreases as the body attempts to keep blood sugar levels from dropping further. Although it varies from person to person, most people will notice symptoms once blood sugar levels drop into the 60’s.
If the symptoms are ignored and blood glucose levels drop below 50 ml/dl brain function is affected. Symptoms then include:
- Behavioral changes
- Confusion
- Drowsiness
- Seizures
- Coma
Tests and Diagnostics
If you believe you are experiencing the symptoms of hypoglycemia, a simple blood test can be conducted in your doctor’s office. (It can also be easily tested using a home glucose meter). A low glucose reading in conjunction with any or all of the symptoms of low blood sugar usually serves as a diagnosis for the disorder in a person who does not have diabetes.
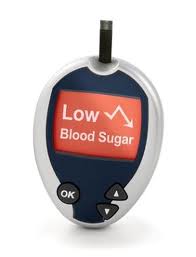
Hypoglycemia is also diagnosed by three key features known as Whipple’s triad. They are:
- Symptoms consistent with hypoglycemia.
- Low plasma glucose concentration.
- Relief of symptoms after the plasma glucose level is raised.
The doctor may perform a glucose tolerance test, or take a blood sugar reading after an overnight fast.
Risk Factors
If the symptoms of hypoglycemia are ignored, serious consequences can occur. The brain relies on glucose for fuel, but if the fuel source is not available the body is able to produce an artificial energy source known as keytones. However, keytones are used only when the body is under sever glucose depletions and can cause some damage to brain cells. Once the body can no longer make keytones and there is no glucose for fuel, the brain will shut down.
Individuals at a higher risk for hypoglycemia:
- Diabetics on a tightly controlled insulin regimen
- People with pancreatic or liver diseases, tumors or other health issues
- Children born to diabetic mothers
- People with endocrine disorders
- People on low carbohydrate diets
- Alcoholics
Prevention Tips
If hypoglycemia is caused by diabetes, talk to your doctor about regulating insulin levels to keep blood glucose levels from dropping too low. Never take more medication than is prescribed, as this can lead to serious issues of low blood sugar.
If you notice symptoms of low blood sugar on a regular basis and you are not a diabetic, the most likely cause is a poor diet, which can be easily prevented. Do not skip meals, eat healthy snacks between meals if needed, and avoid large amounts of alcohol, sugars and carbohydrates. Excessive exercise without adequate food intake can also cause blood sugar levels to drop below normal.
Treatment Options:
Home Remedies:
Vitamins:
Some vitamins are effective in the treatment of hypoglycemia. These are vitamins E, C and B complex. Vitamins C and B increase the body’s tolerance of sugar and carbohydrates, Pantothenic acid and vitamin B6 build back the body’s supply of adrenals, which are often depleted by low sugar levels. Vitamin E improves glycogen storage in tissue and muscles.
Adding foods rich in these vitamins can help control the occurrence of low blood sugar. Supplements are also readily available and can be taken with low risks for side effects. Try taking up to 1600 IU of vitamin E, 50 mg of vitamin B6, and large doses (2,000 to 5,000 mg) of Vitamin C daily. It is extremely difficult of overdose on vitamins, they are beneficial for a variety of health issues, and supplements are generally inexpensive.
Apples and Orange Juice:
Typically, any fruit can aid in raising low blood sugar levels, but one small glass of orange juice or two small apples have been found to be the most effective.
The Low Blood Sugar Diet:
People who experience low blood sugar on a regular basis should base their diet on three basic food groups: grains, seeds and nuts, and vegetable and fruits. Supplement this diet with vegetable oils and milk and dairy products. Helpings of carbohydrates such as refined pastas, starchy potatoes and products made with a lot of white flower should be consumed in moderation. Cooked grains are digested slowly and release sugar into the blood stream in small, steady increments. This will help keep blood sugar levels steady.
Try eating 6 – 8 small meals a day as opposed to 3 large ones. The body will receive a steady supply of nutrition without causing blood sugar levels to rise and drop dramatically. Try to include fiber and protein with each meal because they are broken down into sugars much more slowly.
Look for fresh, as opposed to refined, ingredients. The less processed something is, the less likely it is to cause spikes and valleys in blood sugar levels. Things like white sugar, white flower (and items made with them as a main ingredient) should be eaten only in very small amounts, and never alone. Also avoid coffee, sodas, and alcohol whenever possible.
Try to include as many high fiber, low sugar and fat foods as possible. Switch to whole grains in pastas and breads.
Carb or no carb?
With the rising popularity of low carbohydrate diets, people that regularly experience hypoglycemia may think that eliminating carbohydrates will keep them from feeling the effects of rising and plummeting blood sugar levels. However, not all carbohydrates are the same, and it is not wise to eliminate them completely from your diet.
Simple carbohydrates are broken down into sugars very quickly in the digestive system and are more likely to cause spikes in blood sugar (and subsequently spikes in insulin production). Simple carbohydrates can occur naturally or be the result of processed foods. These include:
- Honey
- Table sugar
- High fructose corn syrup
Complex carbohydrates are essential to the diet. They are absorbed more slowly and are less likely to cause spikes in blood sugar. They include:
- Pastas
- Grains
- Potatoes
Proteins found in animal and legume products are also broken down into sugars for fuel, but they generally take much longer in the digestive system and do not contribute to insulin spikes.
Herbs thought to help regulate blood sugar:
- Angostura bitters
- Artichoke leaves
- Gentian Root
- Bilberry and wild yam are thought to aid in controlling insulin levels.
Pharmaceutical Remedies:
For problems with low blood sugar that are not controlled by diet or are a result of other health problems, some medication may be necessary.
Diazoxide (Proglycem) and streptozotocin (Zanosar) are medications that suppress insulin release from the pancreas.
If hypoglycemia is a result of other issues such as diabetes, pancreatic or liver disease, tumors or hormone deficiencies, the treatment of these conditions with medications prescribed by a healthcare professional will alleviate the symptoms of low blood sugar as well.
The costs and effectiveness of pharmaceutical remedies will depend greatly on the individual condition and prescription.
Surgery:
If hypoglycemia is caused by a tumor in the pancreas or liver, surgery may be necessary. If the tumor is malignant and is inoperable, medications may be able to suppress insulin release from the affected cells. A doctor or an endocrinologist can determine the need for surgery on an individual basis.

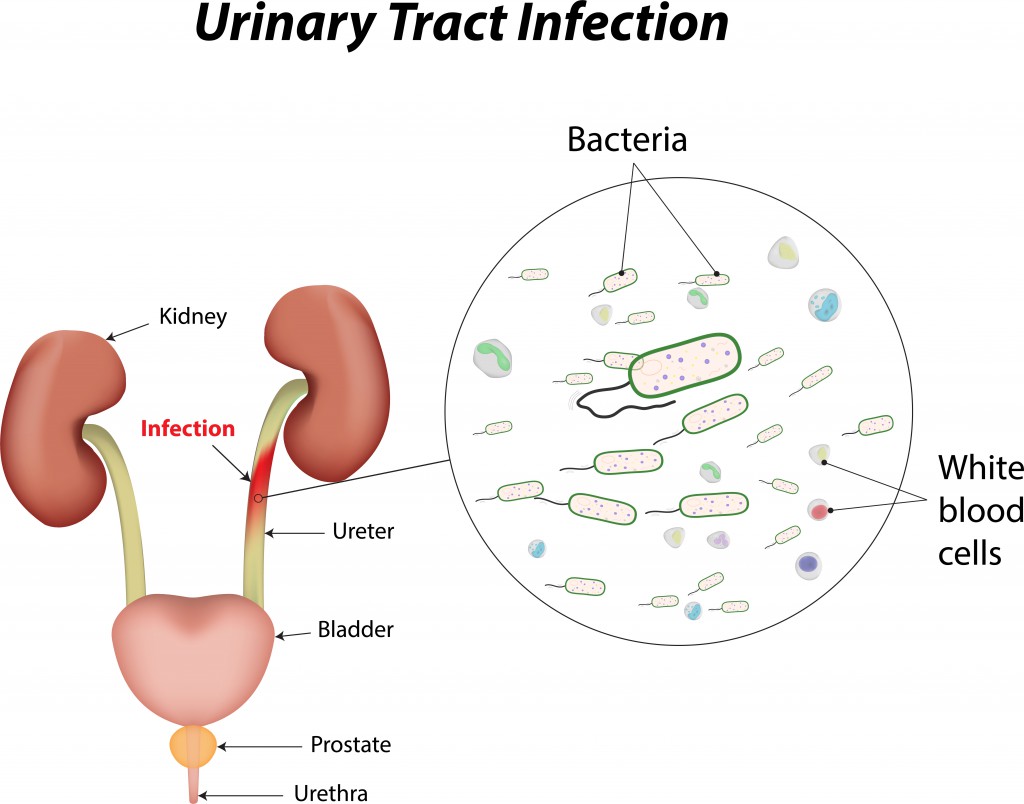
 Urinary tract infections usually occur when germs or bacteria somehow enter the urethra and continue through the urinary tract by multiplying. The multiplying of the bacteria can cause an infection in areas of the urinary system. One specific type of bacteria that can cause urinary tract infections is Escherichia coli (E. coli), which can be found normally in the gastrointestinal tract.
Urinary tract infections usually occur when germs or bacteria somehow enter the urethra and continue through the urinary tract by multiplying. The multiplying of the bacteria can cause an infection in areas of the urinary system. One specific type of bacteria that can cause urinary tract infections is Escherichia coli (E. coli), which can be found normally in the gastrointestinal tract.
 There are several over-the-counter solutions to pain and burning during urination available at large pharmacy chains like CVS or Walgreens and local pharmacies.
There are several over-the-counter solutions to pain and burning during urination available at large pharmacy chains like CVS or Walgreens and local pharmacies.