Fungal infections, which are also known as mycoses, occur when a fungal agent manages to pass through the barriers that are set up to protect the body and establishes an infection. Fungal infections can be classified according to the part of the body that is infected. A superficial mycosis is an infection that affects the outer layers of skin and hair. A cutaneous mycosis infects the epidermal layer of the skin, which is slightly deeper than the parts of the skin that are affected by a superficial infection. Cutaneous infections can also invade deeper into the keratinized layers of the nails and hair. A subcutaneous infection occurs even deeper in the body, in the dermis of the skin, the subcutaneous tissues, the muscle and the fascia. A systemic infection affects the organs of the body.
The part of the body that has been infected by the fungus will affect the type of symptoms that are experienced and the severity of the condition. A superficial mycosis is usually less problematic than a systemic one, for example.
Different types of fungal infection are given different names. Common fungal infections are athlete’s foot, thrush and other yeast infections, ringworm, jock itch, valley fever and nail fungus.
Despite the differences between fungal infections, they are all treated in similar ways, by the application of an antifungal drug. In the same way that antibiotics are used to treat different bacterial infections, antifungal drugs can be used to treat infections caused by fungi. In some cases, however, the infection may also be treated with surgery rather than simply with an antifungal agent alone.
Symptoms
The symptoms of fungal infection can vary a great deal depending on the type of infectious agent that is involved and the part of the body that has been affected.
Tinea versicolor is a common superficial fungal infection that usually occurs in young patients. It creates small light or reddish brown spots that are mainly found on the back, chest, legs and upper arms. There are two forms of this infection, only one of which causes spots that are visible. Other than the spots, there are usually no symptoms and the infected person remains healthy.
Unlike superficial infections, cutaneous infections can create an immune response in the patient. This can lead to pathologic responses and changes in the affected layers of the skin. Roundworm, for example, presents as round scaly red rings on the skin. Fungal organisms that cause cutaneous infections are known as dermatophytes, while the diseases that they cause are often called tinea or ringworm. Despite the name, ringworm is a condition that is caused by a fungus and not an actual worm. The species of fungus that cause this type of infection are Trichophyton, Epidermophyton and Microsporum.
Types of Infections
Subcutaneous fungal infections are usually chronic conditions. They often begin after the skin has been pierced by an injury of some kind, since this allows infectious fungi to penetrate the skin and establish themselves inside. The treatments for subcutaneous infections are usually more drastic than those for less severe infections.
Systemic fungal infections may be either primary or opportunistic. A primary pathogen infects the body independently of any other medical condition, while an opportunistic pathogen can only cause an infection in a body that has already been weakened by something else. Primary fungal pathogens are most likely to enter the body through the lungs, which is where they generally cause their first infection.
This can then be spread to other organs in the body. Most primary pathogens are dimorphic fungi, which means that there are two different forms in the lifecycle. Opportunistic fungal pathogens can only establish an infection when the defenses of the body have been lowered by some sort of immunosuppressive condition. This could be a disease such as AIDS or a metastatic cancer (one that has spread to multiple parts of the body) or a treatment such as immunosuppressant drugs or antibiotics. Aspergillosis, Candidiasis and Cryptococcosis are all opportunistic fungal infections. Systemic infections are the most serious.
Diagnosis
Many fungal infections cause characteristic symptoms that can be used to make a diagnosis. In some cases, laboratory tests may be needed to rule out any other possible causes of the symptoms and to identify the specific fungus that is responsible for the infection.
Causes
Fungal infections occur when a fungus enters the body and causes an infection. The fungus multiplies within the infected part of the body, and may be able to spread to other body parts. In some cases, the fungus requires some help in order to be able to infect the body. Opportunistic systemic fungal pathogens cannot infect a body unless its immune defenses have already been broken down by another infection or disease, or are being suppressed by a medication that is being taken.
Similarly, some subcutaneous infections can only reach the lower levels of the skin where they can establish an infection when a path has been opened up for them by some sort of injury that has penetrated the skin. Other fungal infections can occur without such help. They simply need to come in contact with the skin, or be breathed into the lungs in order to infect the patient.
Fungi come in a number of different forms. Fungal cells are similar to plant cells, and fungi are comparable to plants. They are neither plants nor animals, however, but form their own separate group, with its own unique characteristics. Fungi do not produce their own energy in the same way as plants, and must therefore find food from other sources. Most fungi break down dead material, but others can infect living organisms.
Major Infections
Fungal infections are named after the species of fungus that causes the infection. The major fungal infections are
- aspergillosis (caused by Aspergillus)
- blastomycosis (caused by Blastomyces)
- candidacies (caused by Candida)
- coccidioidomycosis (caused by Coccidioides)
- cryptococcosis (caused by Cryptococcus)
- histoplasmosis (caused by Histoplasma)
- paracoccidiomycosis (caused by Paracoccidioides)
- sporotrichosis (caused by Sporothrix)
- zygomycosis (caused by Zygomycetes).
Each of these conditions is caused by a specific type of fungus. Some other fungal infections cannot be classified in the same way because they can be the result of a number of different types of fungus: chromoblastomycosis, lobomycosis, mycetoma, onychomycosis, various Tinea diseases, piedra, pityriasis versicolor, otomycosis, phaeohyphomycosis and rhinosporidiosis, as well as a number of infections affecting the eyes, skin, hair and nails.
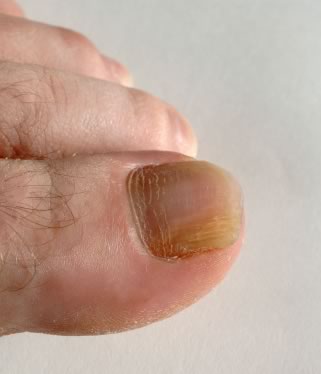
Tinea infections are the most common type of fungal infection. Athlete’s foot is an example of this type of infection. It affects the feet, causing itchiness and flaky skin. It can also spread to the toenails, causing them to thicken and become discolored.
Candida infections, which are also known as thrush, are also very common. Candida usually lives on the body without causing any problems, but sometimes it can cause an infection of the mouth or the vagina.
Prevention
Many types of fungal infections can usually be prevented by following good hygiene practices. Ensuring that the skin is kept clean and dry can help to prevent fungal infections from affecting the skin. It is also important to wash thoroughly after coming into contact with other people or with animals. Infection can be avoided when using public swimming pools and showers by wearing flip-flops to protect the feet. Regularly cleaning sports clothes can also help to prevent fungal infections.
In order to prevent the development of an internal fungal infection, which could be very serious, antifungal drugs are sometimes prescribed as a preventative measure to patients who are in a high-risk group. Regularly taking this medication can prevent an infection from taking hold. Fluconazole is an example of an antifungal drug that can be used to prevent fungal infections in the body.
Treatments
Fungal infections are treated with a type of drug that is known as an antifungal agent. These may be taken either orally or applied to the skin, depending on the sort of infection that is being treated. Most antifungals work by attacking the cell walls of the infectious fungus. Once these have been damaged, the fungus will die. Antifungal drugs work by discriminating between the cells of the body and those of the fungus, but since there can be similarities between these cell types, the drug may sometimes act on a human cell. This can cause adverse side effects.
There are many different types of antifungal drug. Most of these drugs can be classified into the following categories, although there are also some other topical and systemic drugs that do not fit into one of these groups.
- allylamines
- antimetabolites
- azoles
- chitin synthase inhibitors
- glucan synthesis inhibitors
- polyenes
In order to increase the chances of a drug being successful for the treatment of a particular infection, it is important to choose the right drug to combat that particular condition. Different fungal agents will react differently to particular antifungal drugs. Most fungal infections can be treated by multiple drugs, depending upon which one the doctor believes is most suitable for the individual case.
In the same way as bacteria can develop a resistance to antibiotics, infectious fungi can become resistant to antifungal drugs. When a resistant infection occurs, it may need to be treated with an alternate antifungal drug. It will usually be more difficult to get rid of a fungal infection that has developed some resistance to treatment, since if the first choice drug cannot be used, the second choice drug may not be quite as effective.
Applications of Medicine
Topical application of an antifungal agent, that is application onto the skin in the form of a cream or shampoo, can be used to treat fungal infections of the skin and vagina. Drugs that can be used in this way include amorolfine, miconazole, ketoconazole, griseofulvin and sulconazole. In some cases, an antifungal cream may be used in conjunction with another sort of cream, such as a steroid cream, which can reduce the inflammation as the antifungal cream destroys the infection.
Oral application of antifungal drugs can be in the form of liquids, capsules or tablets. Nystatin and amphotericin are taken by mouth, as either lozenges or liquids, but they cannot be absorbed through the digestive system. Instead, they are used to treat fungal infections of the mouth and the throat. Other oral antifungals do need to be absorbed in order to work in other parts of the body. Antifungal medications that work in this way include terbinafine, which is often used to treat tinea infections in the nails, and fluconazole, which is often used as an alternative to topical treatment for vaginal thrush. It can also be used to treat infections within the body. Both terbinafine and fluconazole are taken in the form of tablets.
In some serious cases, the antifungal drug is delivered in the form of an injection. Injectable antifungals include flucytosine, voriconazole, amphotericin, caspofungin and itraconazole.
Subcutaneous infections may require surgical treatment in combination with antifungal drugs. For example, the infected tissue may be removed in a process known as debridement.
Traditional Remedies
There are many traditional cures and remedies that have been used to treat fungal infections. Some of these have some basis in fact, but others are ineffective. While antifungal drugs are usually effective, unless the fungus has developed a resistance to them, these traditional remedies are usually unable to eradicate a fungal infection. They may help to ameliorate the symptoms of the infection, however, and some remedies can help to keep fungal infections at bay.
A scientific study conducted in 1996 found that a number of essential oils and other substances had some antifungal properties. These included allicin (produced from crushed garlic), citronella oil (produced from the leaves of lemongrass), tea tree oil, coconut oil, zinc (when taken as supplements or eaten in foods such as chickpeas and pumpkin seeds), selenium (in supplements or in foods such as Brazil nuts), iodine, orange oil, Neem seed oil, patchouli, lemon myrtle and palmarosa oil.
More recently, a 2009 study discovered that certain chemicals which are found in carnivorous plants such as the Venus flytrap have antifungal properties. These substances could be used in the future to create new antifungal treatments for fungal infections that have become resistant to other therapies.
It may also be possible to help the body to fight off a fungal infection by taking supplements such as vitamins that are believed to be able to give a boost to the immune system. There is no scientific proof that this type of remedy is effective, however.
Prognosis
The prognosis is good for many fungal infections. They can be eradicated with antifungal drugs and will cause no long-term problems. Other fungal infections can cause serious damage, and may even result in the death of the patient. Systemic infections are the most damaging, and the most difficult to cure.
Fungal infections of the nails, skin, mouth and vagina are very common. They are also easily treatable and are usually resolved without causing any serious problems or spreading to other parts of the body.
More serious internal infections usually occur when the immune system is weakened, and they can be much more harmful. They are also much more difficult to treat successfully. In some cases, systemic fungal infections can be life threatening. Systemic infections can also lead to complications. Cryptococcosis, for example, can result in meningitis.
Complications
Antifungal drugs may cause certain side effects. The possible adverse reactions depend upon the specific drug that is being taken. Antifungal shampoos and creams are the safest forms of treatment and very rarely cause any problems. Some people who are particularly sensitive may develop irritation in the area where the medication has been applied. This is most common with creams that are used for vaginal infections. Oral medications are also generally harmless and can usually be bought over the counter because of this. In rare cases, side effects such as problems with the liver or changes to the levels of estrogen in the body may occur after taking this type of medication. Injected medications can have more serious side effects, and are only used in the most serious cases.
Some people may be allergic to certain antifungal drugs. Azole antifungal drugs have resulted in cases of anaphylactic shock, for example. Antifungal drugs may also interact harmfully with other types of medication. Azole antifungals produce adverse reactions when mixed with immunosuppressants, chemotherapy drugs, calcium channel blockers, tricyclic antidepressants, SSRIs, benzodiazapenes and macrolides.
If a fungal infection cannot be cured then it can continue to cause damage to the body and may spread. Systemic fungal infections can be particularly harmful if they are not eradicated, and may even be fatal.
Cost
There is wide variation in the costs of treatments for fungal infections, since the types of treatments that may be necessary can vary enormously. Some topical treatments for mild infections of the skin can be bought over the counter at a drug store for well under $10. Other types of treatment can cost over $200. There are also various antifungal drugs that fall in between these prices. The most expensive antifungal drugs can cost as much as $600, although these costly drugs will only be required in the most serious cases.
If surgical treatment is required, then this will significantly add to the cost.
The essential oils and other traditional remedies for fungal infections are fairly cheap. They can usually be bought for less than $10 at a health food store or other specialist stockist.