What is a Urinary Tract Infection?
The system inside the body responsible for making urine and exporting it out of the body is known as the urinary tract. It is made up of the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra. If germs or bacteria get anywhere into this system, and infection can occur, known as a urinary tract infection.
Acute cystitis is the most common type of urinary tract infection, and it is the inflammation of the bladder. These urinary tract infections are often referred to as bladder infections. Urethritis is the inflammation of the urethra, and is another type of urinary infection. Pyelonephritis is an infection of the upper portion of the urinary tract or kidneys, and is a more serious type of urinary tract infection. If a bladder infection is not properly treated, it can often lead to a more dangerous kidney infection.
Women are more likely than men to get urinary tract infections, possibly due to shorter urethras or the fact the urethra is closer in proximity to the anus, which makes it easier for germs to get to the bladder.
However, it is not impossible for a man to suffer from a urinary tract infection as well, and many elderly men are prone to these infections, possibly due to enlarged prostates.
UTI? Get Remedies Fast!
What are the symptoms of a urinary tract infection?
There are quite a few symptoms of urinary tract infections. Some of the more common symptoms include the need or feeling to frequently urinate, although there may not be much urine that empties the body when you do, or dysuria, which is a burning sensation when urinating.
Urine may also look cloudy or possess a foul odor. Blood and bacteria in the urine are also possible symptoms of urinary tract infections. It is also possible that your belly will feel some tenderness or pain as well. Pain on one side of your back underneath your ribs can also indicate an infection, as this is where your kidneys are located. Fever or chills may also be present.
Often with acute cystitis, pelvic pressure, abdominal discomfort, frequent, painful urination, and a low-grade fever may be found. With pyelonephritis, upper back and side pain is common, as well as high fever, chills, nausea, and vomiting. For those suffering from urethritis, burning while urinating is the main symptom.
What are the causes of a urinary tract infection?
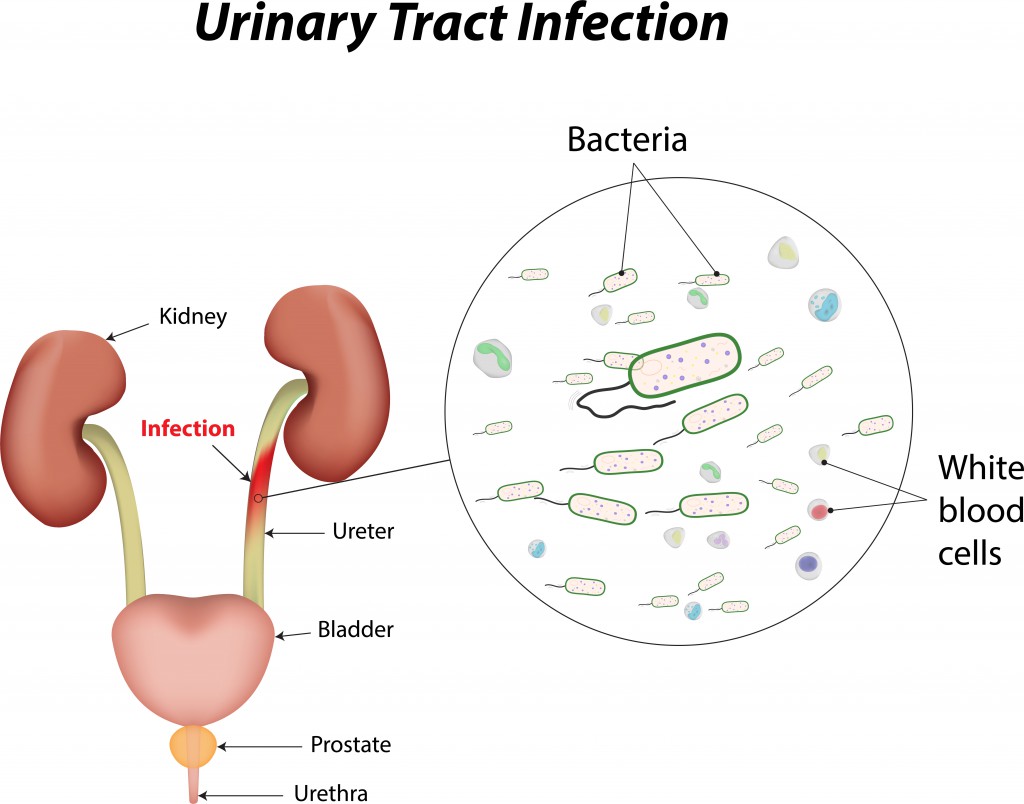
 Urinary tract infections usually occur when germs or bacteria somehow enter the urethra and continue through the urinary tract by multiplying. The multiplying of the bacteria can cause an infection in areas of the urinary system. One specific type of bacteria that can cause urinary tract infections is Escherichia coli (E. coli), which can be found normally in the gastrointestinal tract.
Urinary tract infections usually occur when germs or bacteria somehow enter the urethra and continue through the urinary tract by multiplying. The multiplying of the bacteria can cause an infection in areas of the urinary system. One specific type of bacteria that can cause urinary tract infections is Escherichia coli (E. coli), which can be found normally in the gastrointestinal tract.
Since the urethra is so close to the anus, it is easy for E. coli to enter the urethra and travel up the urinary tract. Improper wiping after using the restroom can contribute to this as well. Women should always wipe front to back, not back to front.
Sexual activity is also a major cause of urinary tract infections. Spermicide and diaphragm use may also contribute to urinary tract infections. Women should try to urinate after sexual intercourse to lessen the likelihood of an infection. Some may even go as far as to shower immediately following intercourse to prevent infections. Some sexually transmitted diseases like herpes, gonorrhea and chlamydia have also been considered as causes of urinary tract infections.
What are the risk factors of a urinary tract infection?
Being female is a risk factor contributing to urinary tract infections. It is approximated that at least half of all women will have a urinary tract infection at some point in her life, and many women have more than one. The female anatomy and shortness of the urethra are leading reasons for females having more infections.
Women that are sexually active are also more prone to urinary tract infections. The urethra can be easily irritated during sexual intercourse, leading to infections. Also, those women using diaphragms and spermicides are more likely to get urinary tract infections.
Pregnant women also have an increased chance of infection, since they are at higher risk of developing asymptomatic bacteriuria, which can turn into urinary tract infections. Some women have even found that using feminine hygiene products that contain deodorants cause them to develop urinary tract infections. Women going through or past menopause may also be at increased risk for infection. This may be due to the fact that the loss of estrogen has thinned the tissue of the urinary tract, allowing for bacteria to harbor more easily.
Men & UTI’s
For men, although it is less common to develop urinary tract infections, it is still possible, especially for those that have problems with their prostate gland. Also, men with an uncircumcised penis may be at higher risk for infections. Men that have intercourse with a woman that has some sort of vaginal infection may develop a urinary tract infection, as well as men that engage in anal intercourse. Infections from HIV can also develop into urinary tract infections.
In both men and women, those with kidney issues, diabetes, or that have the use of catheters in their bladder may also be at increased risk. It is even possible that not drinking enough fluids can lead to urinary tract infections. The more fluids that a person drinks, the more times that person will urinate, which decreases the bacteria in the urinary tract. Some have even suggested that hereditary factors may lead to an increase in urinary tract infections.
What are some ways to prevent urinary tract infections?
Numerous tips are available to help prevent urinary tract infections. First, it is important to drink a lot of liquids, specifically water. This will cause you to urinate frequently, which will rid the urinary tract of bacteria. It is also important to urinate when you need to, and not to hold it. Drinking cranberry juice has also been shown to help prevent urinary tract infections. Some choose to take cranberry capsules instead, which seems to work well too. Avoiding constipation can also prevent urinary tract infections.

Specifically for women, you should always wipe front to back when using the restroom. This will help keep bacteria from the anus from entering the urinary tract. Urinating immediately following sexual intercourse is also helpful in preventing infection.
Drinking a large glass of water following intercourse can also flush out bacteria. Changing sanitary napkins often and not using feminine products with certain deodorizers can also help minimize infections.
Men need to make sure to keep the tip of his penis clean, especially if he is uncircumcised.
The foreskin area of the penis can easily trap and be a haven for bacteria, which can then travel into the urinary tract, thus causing infection. By keeping this area clean, it will minimize on the likelihood of bacteria harboring there.
What are some test and diagnosis considerations?
If you or your doctor suspects that you have a urinary tract infection, he or she will most likely take a urine sample. You will first be instructed to clean your genital area and then submit a sample. The laboratory will then analyze the urine sample, which is called a urinalysis. This simple test will show whether or not you truly have an infection.
If you suffer from recurrent urinary tract infections, other tests may be done to determine the cause of these infections. An abdominal or pelvic ultrasound may be used to produce a picture of the upper abdomen or pelvis to look for causes or problems.
A voiding cystourethrogram may be used as well. It is an x-ray that is taken while you are urinating that can detect issues and problems. A cystoscopy may also be used, which allows the doctor to look inside the bladder and urethra. An intravenous pyelogram is an x-ray test that takes pictures of the kidneys and urinary tract, which can also help diagnose problems.
What are some treatment options for urinary tract infections?
For those suffering from urinary tract infections, the typical method of treatment prescribed by doctors is a dose of antibiotics. Some of the common antibiotics used for urinary tract infections are Amoxicillin (Amoxil, Trimox), Nitrofurantoin (Furadantin, Macrodantin), Ciprofloxacin (Cipro), Levofloxacin (Levaquin), and Sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim (Bactrim).
The amount of dosage depends on many factors, and some may only have to take the medicine for three days, while others may continue for a week or more. The doctor may also describe some type of pain management medication for those who are suffering from painful or burning sensations during urination. These treatment options are affordable, and have generic options to keep the cost low.
 There are several over-the-counter solutions to pain and burning during urination available at large pharmacy chains like CVS or Walgreens and local pharmacies. AZO Urinary Pain Relief® Maximum Strength tablets contain 97.5 mg of phenazopyridine hydrochloride, a urinary tract analgesic, and a 2-day supply can be had for around $10. Some pharmacies also offer their own generic versions which can be had for about half the price.
There are several over-the-counter solutions to pain and burning during urination available at large pharmacy chains like CVS or Walgreens and local pharmacies. AZO Urinary Pain Relief® Maximum Strength tablets contain 97.5 mg of phenazopyridine hydrochloride, a urinary tract analgesic, and a 2-day supply can be had for around $10. Some pharmacies also offer their own generic versions which can be had for about half the price.
If the antibiotic does not seem to help the infection, further evaluation by your doctor may be needed. It may be possible the infection has spread to your kidneys, and would now be considered a kidney infection. There could also be some issues with your immune system that would need to be looked at. There is no surgical option for the treatment of urinary tract infections.
Home Remedies
There are however, many at home remedies for relieving a urinary tract infection. Drinking a lot of water and cranberry juice are probably the most common at home methods. Both of these options are very cost effective and easy to do. Using a warm heating pad on either your back or abdomen may also help with pain management, as well as taking a warm bath or a long shower, which may help as well. It has also been suggested that adding a teaspoon of baking soda to a glass of water and drinking it will neutralize the acidity in the urine, which will ease the pain and symptoms of the urinary tract infection.
Blueberries may also be a natural way to treat, prevent and fight urinary tract infection, as they can fight bacteria much like cranberry juice does. Cranberry juice cocktail has also been shown to work, if you don’t like the taste of pure cranberry juice. Some even choose to take cranberry pills or ActiFruit Max Cran chews instead. Pineapple has also been suggested as a food you can eat to help prevent and minimize infection. Making sure you are getting enough vitamin C is also important, as vitamin C helps keep the bladder healthy and keep bacteria out.
Avoiding caffeine and alcohol will also help minimize the risk of urinary tract infections. Both of these items act as irritants in the bladder, which make an infection more likely. Even using cotton underwear as opposed to other fabrics may help to prevent infections. In case of urinary tract infections, over the counter non-prescription pain relievers will also help with pain management.
All of these home remedies will cost very little and are easy ways to start fighting or preventing urinary tract infections. If you find the at home remedies are not helping, you should see a doctor and consider using antibiotics instead.

No Comments